Photo by Federico Beccari on Unsplash
EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks
Small-scale models optimized for resource-constrained environments
Introduction
EfficientNet is a convolutional neural network model that aims to improve the performance of smaller-scale models for use in resource-constrained environments such as low-power devices or edge devices. The model utilizes advanced techniques such as neural architecture search and specialized building blocks to optimize its performance, and focuses on scaling various aspects of the model to achieve the best results. In this article, we will explore the concepts behind EfficientNet and how it is designed to improve the performance of smaller-scale models.
Problem
There are two problems that this work is addressing:
The effect of the number of layers, channels, and resolutions
Finding the next small-scale model that performs well
For the first problem, there are many papers that improve the model by scaling the number of layers, the number of channels, or the resolution of the image. Some studies on one of the values. Others study two together. However, there were not any that looked at all three of them.
For the second problem, obviously, if we can achieve better performance on smaller models, it would help with computation on low-power devices (e.g., mobiles) or edge devices.
EfficientNet
Mobile Inverted Bottleneck
Mobile inverted bottleneck is the building block for this network. It utilizes the concept of skip-connection, a squeeze-and-excitement mechanism, with depth-wise separable convolution for small parameters.
Neural architecture search (NAS) is used to find the optimal network for this model.
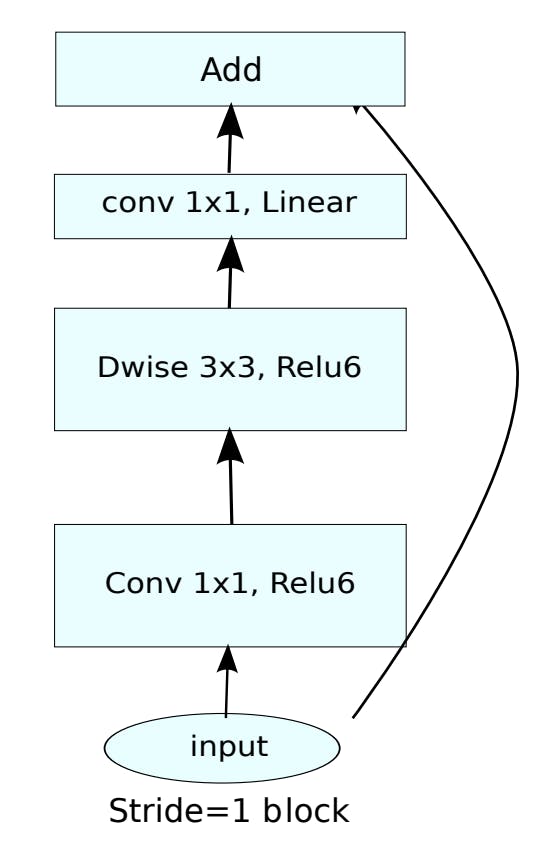
Compound Scaling
This work focuses on three aspects:
depth \(d\): Number of layers.
width \(w\): Number of channels.
resolution \(r\): Image size (Refer to the image size of every layer).
The experiment shows that scaling one of the aspects will improve the performance. However, it quickly reaches its limit and starts to flatten out. Scaling on all three yields the best performance.
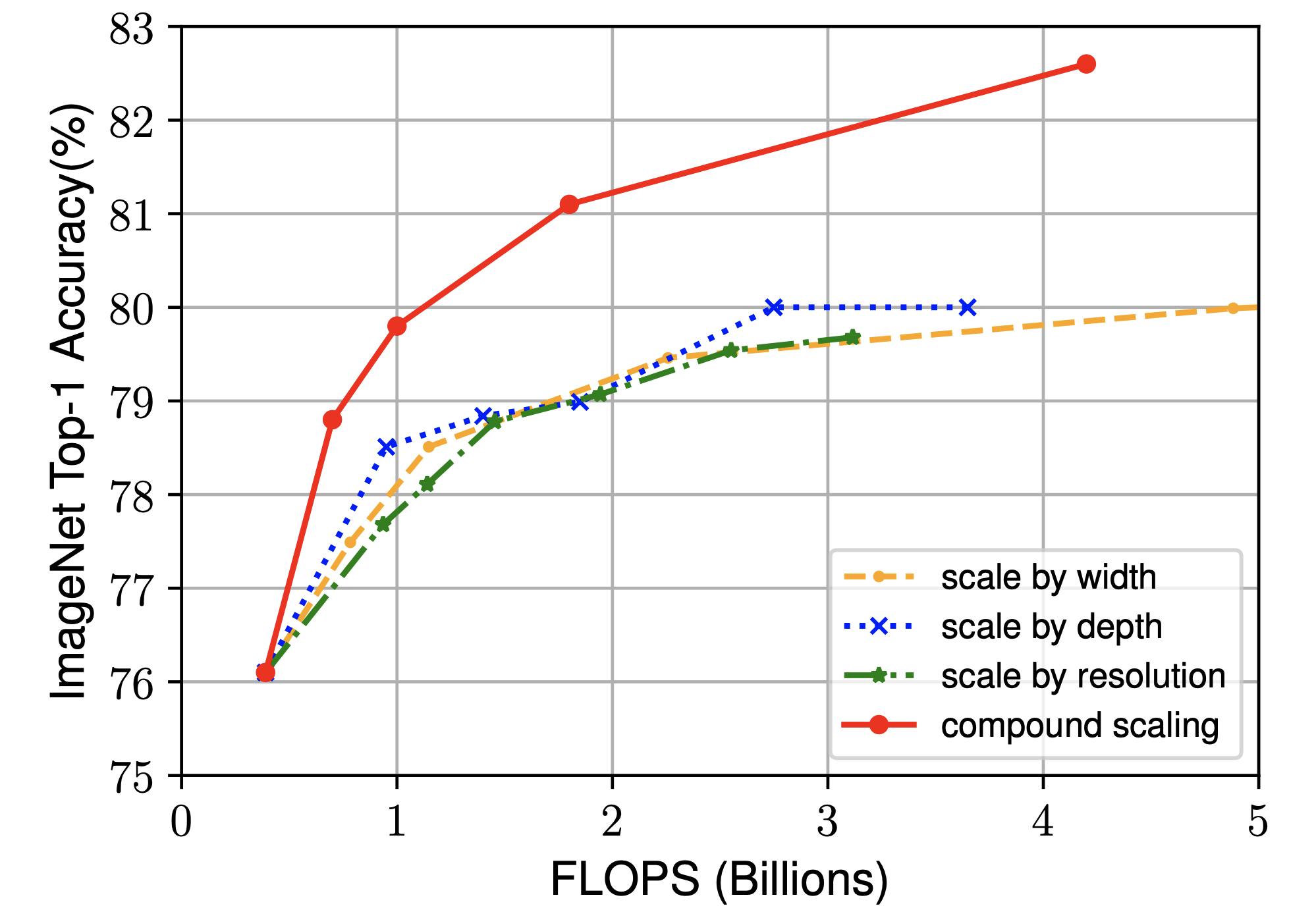
This compound scaling effect is not only applicable to EfficientNet but also to other convolutional models, for instance, ResNet-50 and MobileNet-v2.
Usage
First, a base model is needed. Using that base model, we create another one by scaling up and setting the width, depth, and resolution by multiplying with the following:
depth: \(d = \alpha ^ \phi\)
width: \(w = \beta ^ \phi\)
resolution: \(r = \gamma ^ \phi\)
For simplicity, it is assumed that the three will be scaled by a certain rate. \(\alpha, \beta, \gamma\) are constants. Only \(\phi\) is changed.
The number of depths here does not refer to the total number of layers in the network. Instead, this coefficient refers to the frequency that a block (or a stage) should repeat itself, as shown in the table below.
Let's apply this to EfficientNet. First, EfficientNet-B0 is obtained as the base model. Then, they set (\(\phi = 1\)) and use neural architecture search (NAS) to search for the \(\alpha, \beta, \gamma\) values that best optimize the performance for EfficientNet-B1. Once the three values are obtained, we only need to change \(\phi\) to \(2, 3, ... N\) to scale the model and get EfficientNet-B \(\phi\).
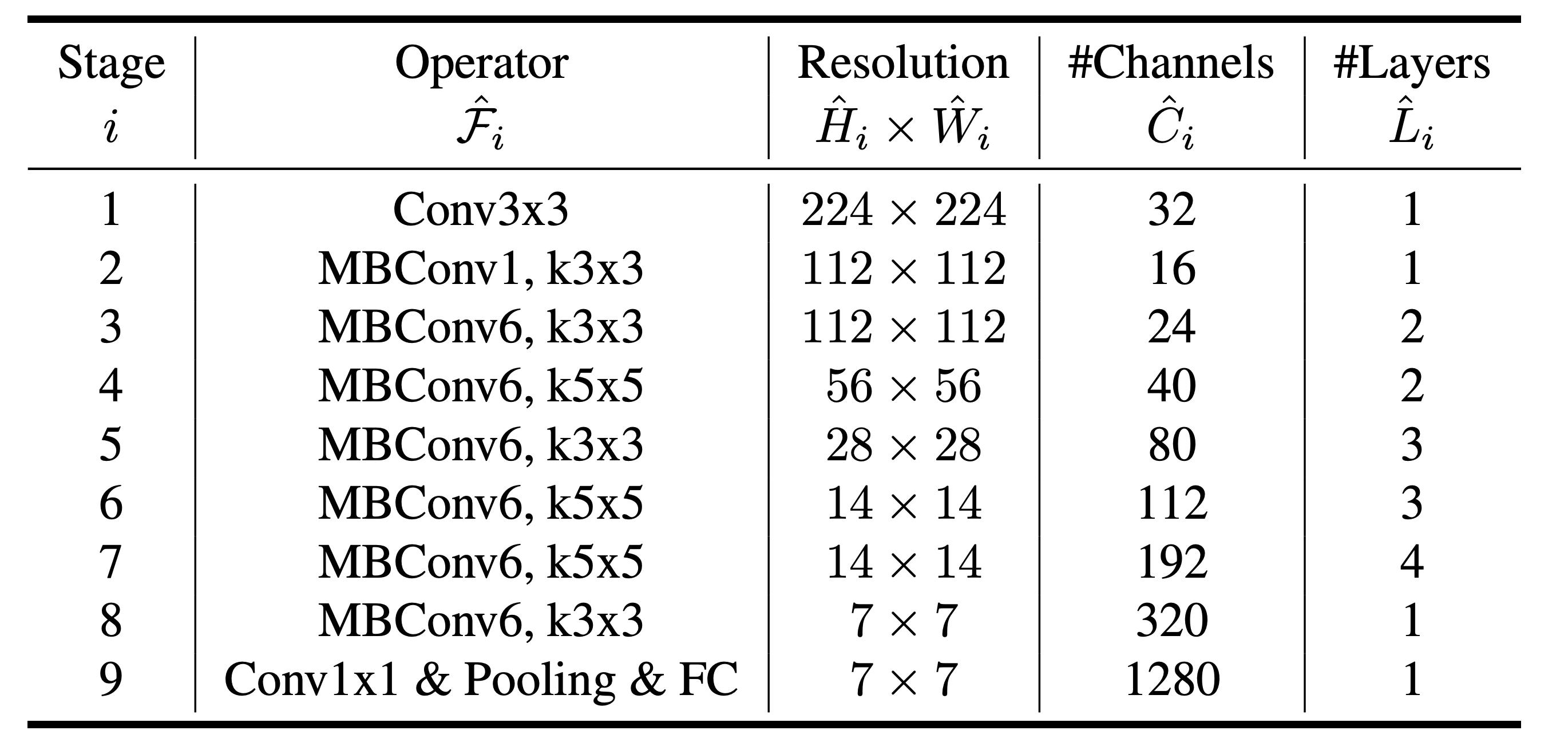
Let's attempt to create EfficientNet-B7. From the paper, the NAS suggests \(\alpha=1.2, \beta=1.1, \text{ and } \gamma=1.1\). With \(\phi=7\):
\(d=(1.2)^7=3.58\)
\(w=r=(1.1)^7=1.95\)
If we look at stage 4, the resolution should now be 109 x 109. The number of channels should be 78, and the number of layers should be 7. Viola, that's how we obtain EfficientNet-B7.
Conclusion
In conclusion, EfficientNet is a convolutional neural network model that is designed to improve performance on smaller models for use on low-power devices or edge devices. The model uses neural architecture search and the Mobile Inverted Bottleneck building block to optimize its performance and focuses on scaling three aspects - depth, width, and resolution - to achieve the best results. The model can be easily scaled by changing the frequency at which blocks or stages repeat, starting with the base model and increasing the scaling factor to obtain higher models. Overall, EfficientNet is a useful tool for improving the performance of smaller-scale models for use in resource-constrained environments.
Key Takeaway
Scale depth, width, and resolution all together achieve better performance than scaling only one of them. It allows information to flow better.
Large resolution requires more channels to capture more features, and it requires more layers to process them properly.
Mobile Inverted Bottleneck is one of the building blocks.
Use neural architecture search (NAS) to help with searching for the right parameters.
References
EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks (Tan. et al, 2019)

